
Egyptian civilization development, history summary
Egyptian civilization refers to the civilization that arose in the Nile embankment and delta region, which is rich in the world's second longest flood of the Nile. Due to the enormous agricultural production in the region, Egypt has enjoyed hegemony (supremacy or hegemony) for a very long time.
1. Before 3100 BC - Prehistoric
2. 3100 BC to 332 BC | Ancient Egypt (Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom)
3. Greece (Hellenism) - Roman period
4. Islamic Era (641 - 1798)
5. Modern Egypt
6. Modern Egyptian Era
1. Before 3100 BC - Prehistoric
Most of Egypt's hunter-gatherer tribes and fishermen's cultures were replaced by agricultural tribes around 10,000 BC. Agricultural tribes usually grind grain into flour, which becomes their staple food. Then, around 6000 BC, changes such as the Earth's axis of rotation and the wet climate of Africa stopped and the Sahara Desert was formed. The tribes that previously lived in the Sahara desert migrated to the banks of the Nile River, and an agricultural settlement economic system was established and a centralized society began to form. Around this time, the Neolithic period (Paleolithic use of excavated stone tools, whereas Neolithic use of interlithic and earthenware) begins throughout the Nile.
Around this time, the 'Badari culture' followed by the 'Nakada culture' developed in the upper part of Egypt, and the 'Merimda culture' 700 years earlier than the 'Badari culture' developed in the lower part. become the whole body Within each Egyptian culture in the upper and southern parts of Egypt, about 30 city-states, each surrounded by walls, enjoy de facto administrative autonomy, and coexist and develop for 2,000 years.
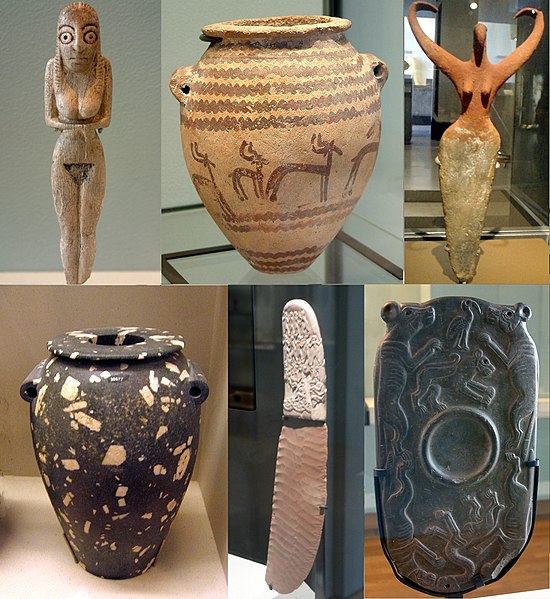

2. 3100 BC to 332 BC | Ancient Egypt (Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom)
The two cultures that were divided into upper and lower parts were unified around 3150 BC by a person named Menes (or Narmes), and the 'Menes Dynasty' began. From this point on, the first unified kingdom of Egypt was established, but several dynasties continued their civilization alternately for about 3,000 years. The Royal Palace of Unification of Egypt is divided into the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom. About 1000 years after Messer's unification is called the Old Kingdom. During the periods of the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom, Egyptian culture flourished and flourished, building a world of originality in religion, art and language for a very long time.
(1). 32nd - 22nd centuries BC | Old Kingdom Period (1st-6th Dynasty)
The capital during this Old Kingdom period was Memphis. During this period, many pyramids were built, with the culmination of the pyramids being the pyramids of Djoser of the 3rd dynasty of Egypt and the pyramids of Giza of the 4th dynasty of Egypt. The pyramids are the most representative tombs of ancient Egypt, but not all tombs and tombs were pyramids, and after the 12th Dynasty, the pyramids are no longer used as tombs.
If we take a quick look at this pyramid around the world, the ziggurat of the Mesopotamian civilization is similar in appearance and structure to the pyramid of Egyptian literature. Of course, the pyramids of Egypt are the most famous, but various pyramids exist in various civilizations throughout history. The strange thing is that it is hard to believe that even these large civilizations have contacted or interacted with each other. Civilizations of different eras and geography have left behind structures such as pyramids in common. There were ziggurats in Mesopotamia 5,000 years ago, and when the pyramids were built in ancient Egypt, there were ziggurats in Mesopotamia. Then, 2,600 years later, the Mayan civilization that arose on the other side of the world also built pyramids. Just as the priests offered sacrifices to the gods in the ziggurats of Mesopotamia, in the Mayan civilization, the priests offered sacrifices to the gods in ziggurat-like structures. And around 250 BC, the Teotihuacan civilization in Central America (100-600 BC) built a huge pyramid. Since this is an area with volcanic eruptions, it is said that hardened lava was used as the material for the pyramid. The Pyramid of Teotihuacan, completed after 50 years, is close to 64 meters high and has 365 steps.
Pharaoh, the king of ancient Egypt, was not only a ruler but also an Egyptian god and had absolute power. The first pyramid was that of the pharaoh Djoser. To effectively express the majesty of the pharaohs, the king's subordinate Imhotep built a six-story pyramid, which is the earliest known pyramid type.
Around 2600 B.C. in the time of Sniperu, the beginning of the 4th Dynasty, the ancient kingdom built a refractive pyramid rather than a step pyramid. The architect at the time who gained engineering experience for this refractive pyramid completes a more complete red pyramid. After Sniperu, Egyptian society became more stable and powerful and later kings began to build pyramids higher. Both King Khufu and King Menkaur build a great pyramid at Giza. The pyramid complex is considered a masterpiece of mankind. This is because, on average, 2.5 tons of stones are piled up, and the number is up to 2.3 million, and the Pyramid of King Khufu, built around 2550 BC, is actually the largest stone building in the world. How the great pyramids were built in the era is still a mystery. In this district of Giza there is a huge sphinx with a lion's body on its head. The Sphinx was created by carving out the entire rocky mountain, so it was maintained for a long time and has a role to protect the pyramids.
With the beginning of the 5th Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, pyramid architecture gradually declined, and the Egyptians concentrated more on building temples for the sun god. Now, it has become a trend to build more sophisticated temples than the old pyramids. Also, when the prosperity and power of the former pharaohs weaken, the crown weakens and the nobles begin to fight for power. Around this time, a sudden drought brought famine on the Nile River, and the Old Kingdom, which had lasted more than 1,000 years, enters a period of turbulence.
(2). 22nd - 21st centuries BC | 1st Intermediate Period (7th-10th Dynasty)
Between the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom, there is a period of chaos called the 'intermediate period'. Due to the excessive longevity of Kings Pepi I and II during the 6th Dynasty, the monarchy was weakened in relation to the succession structure, and the chaos of the local governors started a civil war. At the same time, a dark period came due to sudden extreme drought and famine, and in the vast desert and hot climate, they attacked each other and devoured each other. In the first interim period in AD 146, there were 70 pharaohs for 70 days and 27 pharaohs for 146 years. The 9th and 10th dynasties ruled only around Heracleopolis.
(3). 21st-18th centuries BC | Middle Kingdom (11th - 12th Dynasty)
The chaos of about 140 years of the First Intermediate Period subsided when King Mentuhotep II succeeded in unification during the 11th Dynasty, and the Middle Kingdom era came. He ruled over the new capital, Thebes, but the period of this stable Middle Kingdom located upstream from Memphis did not last long. During this period, military expeditions were also made to Nubia, Syria, and Libya, and new cultures were introduced as exchanges with Asia became active. It is also characteristic of this era that the successor was promoted to pharaoh in advance and made full use of common rule with overlapping reigns.
(4). 18th - 16th centuries BC | Second Intermediate Period (13th - 17th Dynasty)
In 1674 BC, the Hyksos, armed with bronze weapons and chariot skills such as tanks of fire, reconquered Egypt. The 13th and 14th dynasties passed sequentially, and the 15th dynasty started, so the 100-year period of King Hyksos' reign is called the Second Intermediate Period. Their chariots, powerful arrows, armor, metal helmets, and bronze weapons were new arrivals and played an important role in Egypt's subsequent wars of conquest. They adopted revolutionary military technology, but their savage rule plunges Egypt into great conflict again.
(5). 16th-11th centuries BC | New Kingdom (18th~20th Dynasty)

In 1567 BC, when Ahmose I defeated the Hyksos army and established the 18th dynasty, the beginning of the new kingdom era began. The Egyptians, who believed that all things had souls, developed a culture of mummification by carefully keeping the body so that the souls of the dead could return and be resurrected. Mummification, spanning nearly 5,000 years, is one of the most unique traditional ancient Egyptian cultures. Also, most of the kings of the New Kingdom were devoted to territorial expansion. Because the Egyptians could not forget the humiliation of being invaded by the Hyksos. A kind of revenge against them, and the restoration of Egypt's honor, he wins many wars. This meant restoring Egypt's pride.
One of the most expansive pharaohs of the New Kingdom was Hatshepsut of the 18th Dynasty, the only queen of the New Kingdom era. Egypt's heyday was not military power, but rather opened trade routes with Somilia and broadened their horizons through trade. The Egyptians gained a better understanding of the outside world, and everyone lived in abundance. The 18th Dynasty lasted 270 years, and it is famous for its heyday under Ramses II in the 19th Dynasty.
Most of the kings of the 18th Dynasty were great warriors, and the greatest warrior among them was Thutmose III. Across Europe and Asia, the magnitude of the power enjoyed by gods and kings in Egypt's heyday is evident in the great temples. In particular, the oldest and largest surviving temple, the Kar, is a temple that has been extended over a period of one hundred thousand years.
Meanwhile, the god worshiped by almost all kings of Egypt was the god Amon, and at the end of the 18th dynasty, Amenhotep IV carried out drastic reforms in politics and religion. Amenhotep IV abandons the god 'Amon', worships the god 'Aton', changes his name to 'Akhnaton' and moves his capital to Amarna. However, the worship of Aton gradually degenerates into the worship of Akhnaton himself. With these reforms, he tried to suppress religious forces and strengthen the monarchy, but he faced great resistance from the political and religious circles, and eventually the Reformation failed with the death of 'Akhnaton'. However, this monotheism later influences Moses.
Akhenato's successor, the next king, reigns for about ten years and dies at the age of a boy of 18. That is his boy king Tutankhamun. What makes Tutankhamun famous is that the complete tomb of one of the Egyptian pharaohs was discovered by the British in 1922. His tomb contained many untouched treasures, and Tutankhamun's mummified face was covered with a golden mask. Scholars speculate that Tutankhamun's assassination was because Tutankhamun's body was smashed hard on one side of his head and broken bones.
If the ancient kingdom has mysteries that cannot be accessed due to a lack of material, the new kingdom has the largest land and splendid culture. If Ramses II was a representative pharaoh of the heyday of the new kingdom of the 19th Dynasty, which began in 1318 BC, Ramses ruled for about 66 years and built many monuments. A typical example is the Temple of Abu Simbel with four huge statues. This temple is a cave temple made by excavating a rock wall. The four 20m high statues are all statues of the family of Ramses II, who wanted to achieve great things.
Meanwhile, during the reign of Ramses III, the first 'strike' in the history of the dynasty took place. When the salaries that were due to be paid to the workers were not paid during the construction of the burial temple of Ramses III, the workers went on strike saying they could not work until the wages were paid. The strike was successful and the workers were paid their overdue salaries normally.
(6). 11th-4th centuries BC | 3rd Intermediate Period, End of Ancient Egypt (21st-29th Dynasty)
The 19th Dynasty collapsed due to succession issues, the 20th Dynasty emerged, and Libya and the Sea Peoples invaded Egypt. (Professional Civilization Destroyer <Sea People>: Annihilated after destroying the mighty Hittite Empire and causing great damage to Egypt) In the end, Lydia of the sea people and the alien dynasties of Nubia entered. The age of glory that seemed to have no end of the most splendid age of the new kingdom of ancient Egypt gradually collapses, and the age of prosperity of the new kingdom disappears from behind the scenes of history.
After nearly four centuries of turmoil from foreign control, Egypt entered the last dynasty and achieved independence with the help of Assyria. From the 7th century BC (664), the last dynasty, the 26th dynasty (Sais dynasty, Merchant dynasty), constantly struggles to develop Egypt, which is stagnant. The first attempt to build a canal connecting the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, it will become a base for the construction of the Suez Canal in future generations.
3. Greece (Hellenism) - Roman period
(1). 332 BC to 30 BC | Hellenistic period (Prolemaic dynasty)
It is now descending into the 30th Dynasty of Egypt. In 525 BC, the most powerful enemy of Persia invaded Egypt and declared Egypt a city of the Persian Empire. Darius I resumes construction of the canal (Suez Canal) to better govern Egypt. But tired of the harsh Persian rule, the Egyptians fought endlessly for independence. The Egyptians, who achieved brief independence (28-30 dynasties) with the decline of Persia, but did not succeed in resistance in the end, hoped that other countries would overthrow Persia. Eventually, Alexander the Great defeated the Persians in Macedonia, and Egypt was finally freed from Persian domination. In 332 BC, Alexander of Macedon defeated Persia and liberated Egypt, and the Egyptians warmly welcomed Alexander and treated him. Alexander also respected Egypt's religion and traditions, and the Egyptians welcomed him as king. Alexander ushered in the Hellenistic era throughout the empire, including Egypt. The Hellenistic period was the period when Greek culture reached its peak in ancient society, and Alexandria, located on the Mediterranean coast, became the center of the Mediterranean for hundreds of years as Egyptian culture gradually changed.
After Alexander's death, his closest ally, Ptolemy I, ruled Egypt, and the Ptolemaic dynasty began. The Macedonian Prolemaic dynasty maintained continuity with the existing Egypt. The construction of the 100-meter-tall Pharos Lighthouse, one of the Seven Wonders of the World, from the Library of Alexandria in the capital of Alexandria in 288 BC indicates that it was the most advanced period of civilization in Egypt. The last pharaoh of the Prolemaic dynasty was Cleopatra. However, as political upheaval and corruption deepened within the royal family at the end of their reign, the Egyptians rioted several times, weakened and eventually conquered by Rome.
(2). 30 BC - 641 AD | Roman Empire era
Although the Roman hero Caesar took control of Egypt, he protected the Egyptian throne and its independence. However, when a Roman, not an Egyptian, ascended the throne, the pharaoh was completely cut off in Egypt, and Egypt was reduced to the lord of Rome. Egypt, as a lord of a province in Rome, endlessly supplied wheat and papyrus to the empire, and Christianity began to flourish after Christianity became the state religion of the Roman Empire. The Egyptians, who lived as anti-slaves in Egypt, rioted several times.
The decisive reason for the failure of Rome to assimilate Egypt was that it did not respect the Egyptian gods as did the Ptolemaic dynasty. This was a big change for Egypt. After that, a mixture of traditional culture and Roman, Greek, Christian, and Islamic culture took root in Egyptian culture. Because the Egyptians did not specifically object to it.
4. Islamic Era (641 - 1798)

(1). Unified Islamic Empire
After the rise of Islam, it was invaded by Arabs around 640 AD and came under Arab rule. Even with the advent of Islam, Egypt undergoes major changes. As a result, Roman, Greek, Christian, and Islamic cultures are mixed with the existing Egyptian culture, laying down the roots of the current Egyptian culture. What has not changed, however, is that Egypt is still the most prosperous, most prosperous, and Altoran-like core region and has continued to prosper under each dynasty.
Amur, the Muslim empire that ruled Egypt, was fascinated by its beautiful capital, Alexandria. However, whenever the Nile flooded, the road to the Islamic Empire was cut off, eventually establishing a new city near Memphis Pustat. For the next three centuries, it was established as the administrative capital and commercial center. Arabs settled in Egypt through the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties of the Islamic Empire. Existing Egyptians, competing with the Arabs, abandon their existing religions and convert to Islam in order to rise to the ruling class, and Arabic and Islam become the languages and religions of most Egyptians. (About 90% of Egyptians today are Muslim and about 10% are Christian)
(2). The Fatima (963–1169), the Ayyuves (1169–1252), and the Crusades
At the beginning of the 10th century (969), Egypt entered the reign of the Shi'ite Fatima dynasty that arose in Tunisia. They insisted that only descendants of Ali like them could become Muslim leaders, and they made Egypt their new center and the fortified city of Cairo as their capital. As Cairo gradually develops into a metropolis, one of the oldest universities in the world, Al-Azhar University (established in 972, established in 982, is the oldest university in the world). Literally translated, the university's name means 'the most blossoming'. The Fatima dynasty, which had enjoyed a prosperous founding, was eventually overthrown by the Crusaders and destroyed by Saladin.
In 1169, Sultan Saladin established the Ayyub dynasty and made Cairo its capital. With this, the Shia era came to an end and the Sunni era returned. The war with the Crusades went through several truce and war until the end of the Ayyubu dynasty.
(3). Mamluk dynasty (1250-1517)
Then again in 1250, the Mamluk army, who had been active in the Crusades, staged a coup d'état to establish the Mamluk dynasty and overthrow the Ayuvid dynasty. In 1250, the Muslim Mamluk dynasty, ruled by slaves, began. By many standards, "slaves" of this era (many Turks and Circesians ) were granted marriage, private property, freedom of religion, were even permitted to participate in public office, and encouraged to emancipate slaves. Even in the case of the caliphs, there were not a few cases of reviving female slaves. In some cases, the father passed power to his son, but in most cases the victor in the power struggle took the place of the sultan.
Despite many Arab revolts, the Mamluk dynasty rose to power by defeating the Il Khanate of Hulagu in Mongolia at the Battle of Ain Jalut (1260) and restoring the Abbas Khalifa in Baghdad the following year. The Mamluk's struggle saved the Islamic world from a catastrophic crisis that could disappear. After that, the Mamluk dynasty enjoyed great prosperity by controlling the commerce of the Mediterranean as the actual suzerain of Islam.
In 1382, the royal family was replaced by the Bahri Mamluks, mainly Turkic, with the Burj Mamluks, who were the mainstays of the West Cassians and Greeks. However, the Mamluk dynasty lost Damascus to Timur 's strength and only escaped the occupation as Timur planned an expedition to China. However, with the fall of the Timur Empire, the Mamluks regained their power. The Mamluks boasted a strong naval power in the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea until just before their destruction.
(4). Ottoman Empire
In the early 15th century, the prosperous Mamluk dynasty was also severely weakened by intermediary trade when Portugal discovered a sea route to India. In 1492, a deadly plague broke out, killing more than 10,000 people every day. At the end of the Mamluk dynasty, excessive tax evasion and royal luxury were repeated, and it was destroyed by the Ottoman Turks in 1516. The cavalry-centered Mamluks were no match for the Ottomans armed with cannons and musket rifles, weapons that had already killed the Eastern Roman Empire. The following year, Egypt became the lord of the Ottoman Empire.
Egypt, which was a prosperous province of the Ottoman Empire, and the Ottoman Empire also weakened over time, and warlords (mamluks, who did not disappear) became dominant, and even declared independence during Ali 'Bei' (military leader) (1770). Then, in June 1798, during Napoleon 's campaign in Egypt , the warlords and the pro-Ottoman governors were crushed together, and briefly entered the French sphere of influence. French troops withdrew in 1801, but in the process, the Rosetta Stone was discovered in 1799, and Egyptian culture was once again recognized.
Napoleon's expedition briefly placed Egypt under French influence. During the brief French occupation, revolutionary ideas flowed into Egypt, and the Egyptians began an uprising. As time passes, a figure who will remain in the modern history of Egypt and the Arab comes to mind.
5. Modern Egypt

Egypt became independent in 1805 when Muhammad Ali, the commander of Albania, became the governor of Egypt with the support and revolution of the people. Muhammad Ali established control over Egypt by purging the Mamluks, who had ruled Egypt since 1250, and gaining discretion in military activities. He also had active contacts with the West and promoted modernization to develop military power. And in 1832, it completely separated from the Ottoman Empire by conquering the Levant and Hejaz . In addition, it completed the 'Completion of the Transverse Railroad' and the opening of the Suez Canal in Egypt, which are milestones in world transportation. Afterwards, Egypt developed greatly through modernization, and during the Civil War , it benefited enormously from the surge in cotton prices.
However , as US cotton began to pour out in earnest, it fell into financial difficulties. Thousands of Egyptians died from overwork and malnutrition, and governments went bankrupt as a result of excessive forced labor . In the end, he had to sell his shares to Britain, which was coveting the Suez Canal. By gaining control of the Suez Canal, Britain became increasingly involved in Egypt's internal affairs. In the end, after the British forces suppressed the internal rebellion in 1882, Britain attempted to annex the country in 1914. Egypt's attempts to make Egypt a royal colony eventually failed, but Egypt became a complete British protectorate.
In 1919, Egyptians, outraged by British rule, revolted for independence and finally became the Kingdom of Egypt in 1922, but in 1936 British troops were still stationed in the Suez Canal, will be dragged
Meanwhile, Egyptian intellectuals who witnessed modern Napoleon's invasion of Egypt were greatly shocked by the technological gap between the West and Egypt, and began to seek the modernization of Islamic thought. Muhammad Abdu , who was the Sheikh of Al-Azhar University , introduced the Western modernist philosophy to Islam and revitalized the Mutazila School , which had been extinct in the Sunni world since the Middle Ages, thereby establishing the origin of the Islamic Modernism School. Afterwards, Islamic modernism developed centered on progressive intellectuals in modern Egypt, and it influenced the modernization and intellectual development of other Islamic countries.
In the 19th century, Islamic modernism in Egypt had a profound impact on secularism, Salafism , and Islamism in the Islamic world. Taha Hussein, an Egyptian writer with secular-nationalist tendencies in the 20th century , wrote novels that completely contradicted the Abrahamic religious values of the past, which criticized Moses and Israel from the perspective of the pharaohs, and led the reevaluation of Hypatia , a disciple of Muhammad Abdu and Syrian Islamic modernist scholar Rashid Rida laid the foundation for modern Salafism . He understood Islamic modernism from the perspective of the Egyptian people, who had strong anti-Western sentiments. Hassan al-Bannah founded the Muslim Brotherhood by combining Leninism 's popular liberation theory and methodology with traditional Islamic thought and heralded the beginning of Islamism.
6. Modern Egyptian Era
(1). The Age of Gamal Abdel Nasser (1952-1971)
Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Egypt and Jordan formed the Arab Coalition and launched an offensive against Israel's declaration of independence, and the so-called First Middle East War broke out. At first glance, the battle between the weak Israeli army and the British-educated regular troops of the five Arab countries might seem like a gameless game, but in the end, the Israeli army defended the two cities from despair, and the Arab Allies were divided due to mutual distrust, eventually Farouk. I defeated 1 year old.
In 1952, when Nasser, an Egyptian soldier, led a coup d'état and became president in 1956, Egypt's monarchy disappeared and the country entered an era of chaos. Initiation of the Republic Nasser declared the nationalization of the Suez Canal owned by Britain and France in protest, and imposed a curfew on ships, and Israel, France and Britain attacked Egypt. This is the Second Middle East War. At the time, the U.S. government was outraged that it had waged a violent war without consulting the three countries, and the intervention of the United Nations ended the war in 1957, which resulted in Britain and France completely losing ownership of the Suez Canal, and Egypt winning the war. It was unified around Arab nationalism.
As a result, British influence completely disappeared from Egypt, and as a result, the stock prices of Egypt and Nasser soared, and, along with India , became the head of the Third World.
Nasser In 1958, Egypt and Syria merged into one country to form an Arab republic, which caused problems in the unification of several countries. Jordan and Syria win a grand victory in just six days. This is the Third Middle East War, also known as the Six Day War. However, the dream of annexation did not come true and it was split up again and returned to the original state of the Republic of Egypt.
(2). Anwar Sadat (1971–1981) and the era of Hosni Mubarak (1981–2011)
In 1971 Anwar Sadat became president. After the Fourth Middle East War, OPEC countries, which are oil exporting countries in the Middle East, reduced oil exports and raised oil prices, causing a global oil shock. In 1981 Sadat was assassinated by Islamic extremists. Then Vice President Mubarak became president and wielded an iron fist for 30 years.
(3). Egyptian Revolution (2011), and the period of Abdel Fatah el-Sisi (2013-)
In the 2011 Arab Spring pro-democracy protests, Mubarak was overthrown and Muhammad Morsi, who was founded as a democracy, was elected. Egypt's first elected president of the Arab Republic. But secularists and Muslims continued to clash. (Secularism: Let's Separate Politics and Religion) (Islamic Fundamentalism: Let's Maintain the Purity of Islam throughout Politics and Society)
A year after he took office, he overthrows the secularly supported Islamic Morsi regime in 2014, which led to massive anti-government protests. El-Sisi has been leading Egypt since his election as president.
'I. 인문학 (Humanities) > 1- 역사 (History)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Korean origin] The origin of "Yipan-sapan" (0) | 2022.05.24 |
|---|---|
| [History] Summary of Mesopotamian Civilization (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| [Christmas] Summary of the origins of the Christmas tree (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| [History] What is the background of the history of Ukraine and Russia's gunpowder? NATO membership? (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| [역사] 우크라이나 역사, 러시아의 화약고가 된 배경은? 나토 가입여부? (0) | 2022.03.02 |




댓글