[Bitcoin] Bitcoin history, origin, mining, compensation, tax summary

1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was unveiled in October 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto in a 9 - page paper entitled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System " . On January 3 , 2009 , Bitcoin became the first issued Genesis Block, and on February 11 , 2009 , the Bitcoin Core v0.1 program was released . And while making the disclosure, Satoshi Nakamoto said , " The The root issue is all the trust you need to make it work . Central banks must be trusted not to devalue their currencies , but the history of fiat currencies is full of violations of that trust . ” The message "EThe Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks" was left in the Genesis Block transaction .
The unofficial code is 'XBT' or 'BTC' , and in Korea, it is abbreviated as 'Bitco ' , ' Bit ' , and ' Meojang ' . Cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin is not a legal currency, so it is not a standardized code such as ISO . 'BTC' , the most commonly used three - letter abbreviation, is simply an abbreviation of 'BiTCoin' , and ' XBT ' is an ISO 4217 -style naming convention. However , it is also not official code .

In most exchanges, only the blockchain that runs the 'Bitcoin Core' client led by the Bitcoin developer is called ' Bitcoin ' .
Unlike existing currencies, fast and safe transactions between individuals ( P2P) are possible without the intervention of the government , central bank, or financial institutions , and unlike existing currencies that can be printed more if the government wants it , the maximum issuance is limited .
Bitcoin , like most cryptocurrencies , has an extremely unstable market price, so it is meaningless to write about the market price as of several years and months . The first price recorded in this document was 8.35 million won per 1 BTC as of November 5 , 2017 , and the highest price was over 20 million won as of December 2017 . January 1 , 2019 _ On a daily basis, 1BTC = 4.13 million won . If you are curious about the current price, just type " Bitcoin " into the Google search bar and the current price of 1 Bitcoin will be displayed in won without pressing Enter .

The amount of currency to be issued over the next 100 years is predetermined , and only 21 million will be issued . Currently, about 15 million copies have been issued (as of February 2, 2015 ) , and 6 million more are expected to be issued in the future . Although the number is not enough to be used as a world currency, 1 BTC equals 8 decimal places , i.e.
10^{-8}
10
−8
BTC = 0.00000001
Dividends up to 0.00000001BTC are possible . Since the total amount of all bitcoins to be issued in the future is 21 million , as a result, 21,000,000 * 100,000,000 = 2,100,000,000,000,000 (2100 trillion ) Satoshi can be circulated as of the present day .
Also , contrary to what many people misunderstand , it is not an inherent limitation of Bitcoin that the minimum unit of Bitcoin is 8 decimal places . When more money is needed , it is possible to revise the trading protocol to increase the number of digits limit . Still, 1 satoshi has a very small value equal to 0.02 US cents , so unless Bitcoin becomes much more popular than it is now . It looks like it will be a unit that has little to do with day-to-day trading for quite some time .
Although it can be split only in theory , this will lead to a decrease in the value of Bitcoin, so the coin itself may be split ( hard fork ) by opposing forces . Since Ethereum was already split in two in 2016 and showed this risk , it was considered as an unsettling factor when Bitcoin Cash was listed before and after August 1 , 2017 . In fact , after the split , the price of Bitcoin Cash remained stagnant , while the price of Bitcoin rose sharply, seeming to completely shake off the anxiety .
The detailed unit of Bitcoin is as follows .
| 1 BTC | Bitcoin (Bitcoin) |
| 0.01 BTC | 1cBTC (Centicoin, Centicoin) |
| 0.001 BTC | 1mBTC (millicoin, millicoin) |
| 0.000001 BTC | 1μBTC (microcoin, microcoin) or (bits, bits) |
| 0.00000001 BTC | 1 satoshi (satoshi, satoshi) |
Unlike the recently created blockchain -based coins , they are focused on payment or transaction - related systems , that is , their functions as money . For example , Ethereum has a platform function that can be developed into various applications, and accordingly , many coins such as Basic Attention Token (BAT), Golem (GOLEM), Augur ( AUGUR ), and Gnosis are created . platform was provided . Bitcoin was the first Since it is a cryptocurrency created , there is such a thing , and focusing on one function is not a bad thing . However , gradually , there is a problem with the transmission speed and the monetary function is not fully implemented , so many sub - products such as Bitcoin Cash , Litecoin, and Bitgeny appear . The birth of Bitcoin Cash was largely driven by the struggle for interests among miners .

2. What is Mining?
There are generally three ways to earn Bitcoin . In other words , buying it from an exchange, receiving it in return for providing goods and services, and mining new bitcoins . Mining refers to the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin's public ledger, called a blockchain . The reason for the existence of mining is to verify the correctness of all transactions and ensure that all participants on the network use this ledger. It is intended to be read . It is also used to distinguish between legitimate Bitcoin transactions and re = spending money spent elsewhere .
- Mining — The process of recording performance using computer processing power.
- Blockchain — A decentralized public ledger where all Bitcoin transactions are recorded. The reason why such a network is called a blockchain is that blocks are connected like a chain, which refers to a list of all transactions made during a certain period of time. When a block of a transaction is created, miners record it. They apply complex mathematical formulas to this block of information and later break it down into a 'hash', a sequence of letters and numbers that appears to be random.
- Hash — A unique random string of fixed length generated based on the given data. A hash does not consist solely of information about a block of transactions , but also other data . Most importantly , it also includes hashes of past blocks stored on the blockchain . It's not that difficult to generate a hash from a collection of data , such as a transaction block , but it 's nearly impossible to find out what data was used by looking at the hash string . Moreover , every hash is unique. Changing just one character in a Bitcoin block will change the entire hash string .
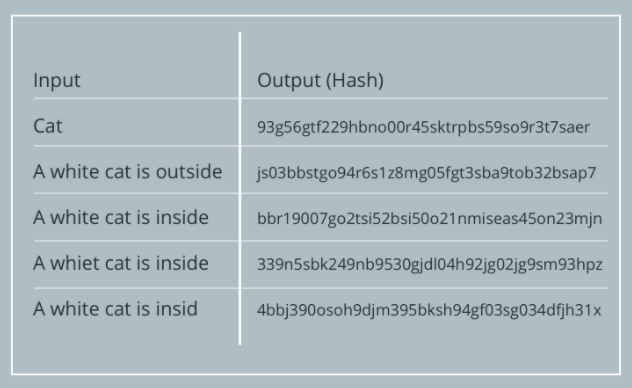
As you can see from the example above, the hash is always the same length no matter how much data is used as input . Due to these characteristics, hash acts like a digital wax seal . When someone touches a transaction block, this hash is changed immediately, and the order of all other hashes on the blockchain is also changed . Therefore , it is not possible to attempt fraud within the blockchain network . In this case, it can be caught very easily .
- Rewards — In a nutshell, miners are contributing to the Bitcoin community by doing the job of verifying every transaction and thereby ensuring that every transaction is correct . Miners are rewarded when a new transaction is ' sealed -off' ( i.e. if the miner has successfully created the correct hash sequence ) . As of October 2017 , the mining reward was set at 12.5 BTC per block . and this amount is to be halved every 210,000 blocks . _ _ The overall number of bitcoin issuance is limited, so the more coins are mined, the higher their value will inevitably increase . Therefore , the number of bitcoins per block will inevitably decrease , but the reward value given to miners will be the same or higher than before . Theoretically, hashes can be derived from various kinds of information . It is very easy to produce, and anything you can do with a computer . That 's why the Bitcoin network had to make this process difficult to ensure that users did n't have to generate hashes from thousands of blocks of transactions every second and take multiple BTC every few minutes .

- Complexity — This is done through so-called 'Proof of Work' (PoW). This refers to a system that requests a certain task from a service requester, and in many cases refers to the processing time of the computer. Generating proof-of-work is a highly random process that requires considerable trial and error to generate valid proof-of-work. In Bitcoin, hashes serve as such proof-of-work.
- Proof - of-Work — A concept that refers to the process of processing the work requested by a service requester in order to prevent fraudulent activity , usually referring to the processing time of a computer . In order to make mining activities more difficult , something called ' Bitcoin Difficulty ' is implemented . This is a measure of how difficult it is to find new blocks compared to the easiest mining methods .
- Bitcoin Mining Difficulty — A measure of how difficult it is to generate an accurate hash . This metric is recalculated for each processing of 2016 blocks . _ The reason for introducing this method is to keep the time required to mine one block constant for about 10 minutes . As more and more miners participate in the network , the block generation rate will inevitably increase . So , after the difficulty is recalculated , the difficulty must be increased to lower the block generation rate again . Blocks that do not reach a certain level of difficulty , created by highly fraudulent miners , are rejected by other participants on the network and thus have no value . Therefore , this process requires a considerable amount of effort, and through all these processes , new money is gradually will be created The rate at which new coins are issued is comparable to the rate at which primary commodities such as gold are mined and produced , hence the term mining .

3. Bitcoin Tax
On the 25th , Elon Musk , CEO of Tesla , an American electric vehicle company , shook the cryptocurrency ( virtual asset ) market once again . He tweeted that in the US you can now buy Tesla electric cars with Bitcoin ( BTC) . Tesla is also planning to introduce Bitcoin payments outside the US . Despite the great news, the price of Bitcoin fell on that day . On the one hand , Bitcoin The news that buying a Tesla may cost you more in taxes than if you bought it with cash is the cause of the Bitcoin price drop . From January 1 of next year , domestic investors will also have to pay tax if they earn more than 2.5 million won a year from cryptocurrency investment . The government classifies cryptocurrency trading profits as other income and imposes a 20% tax . After adding local taxes, the actual tax rate is 22%.
'II. 경제학 (Economics) > 2- 암호화폐 (Cryptocurrency)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Ethereum] What is Ethereum, features of Ethereum, and Ethereum wallet summary (0) | 2022.07.29 |
|---|---|
| [이더리움] 이더리움이란, 이더리움 특징, 이더리움 지갑 총정리 (6) | 2022.01.21 |
| [비트코인] 비트코인 역사, 유래, 채굴, 보상, 세금 총정리 (0) | 2022.01.12 |



댓글